What Are the Components to Building an Effective Csirt Team?
A reckoner security incident response team, or CSIRT, is a group of IT professionals that provides an arrangement with services and back up surrounding the assessment, management and prevention of cybersecurity-related emergencies, equally well every bit coordination of incident response efforts.
The main goal of a CSIRT is to respond to calculator security incidents quickly and efficiently, thus regaining command and minimizing damage. This involves following National Found of Standards and Technology's (NIST) 4 phases of incident response:
- preparation
- detection and analysis
- containment, eradication and recovery
- post-incident activity
To do and then, CSIRTs may take on many responsibilities, including the post-obit:
- create and update incident response plans;
- maintain and communicate information to internal and external entities;
- identify, assess and analyze incidents;
- coordinate and communicate response efforts;
- remediate incidents;
- report on incidents;
- manage audits;
- review security policies; and
- recommend changes to prevent futurity incidents.
A primal assumption of this definition is that a CSIRT is an organized entity with a defined mission, structure, and roles and responsibilities. This assumption excludes any advertising hoc or informal incident response activeness that does not have a defined constituency or documented roles and responsibilities. This supposition is driven by the belief that, without a formalized incident response capability, it is non possible to deliver constructive incident response.
The Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams, an international clan of incident response teams, released the "Kickoff CSIRT Framework." This detailed document builds on Computer Emergency Response Team Coordination Heart (CERT/CC) guidance that has been used since the tardily 1980s. The framework also outlines service areas CSIRTs could offering constituents, including information security event management, infosec incident management, vulnerability direction, situational awareness and knowledge transfer.
CSIRT attributes and processes
While every CSIRT is unique to its organization, in full general, CSIRTs accept 3 attributes that differentiate them from other incident response teams: their mission argument, constituency and list of services.
Mission statement
The CSIRT mission is a statement of purpose or its reason for existing. A CSIRT's mission defines its areas of responsibleness and serves to set expectations with its constituency.
An example CSIRT mission statement may be: "Information technology is the mission of XYZ CSIRT to protect XYZ Corp. by creating and maintaining the capability of detecting, responding and resolving figurer and information security incidents."
Constituency
A CSIRT constituency must be clearly defined. This is the customer base or recipients of incident response services. The constituency is assumed to be unique to a given CSIRT and is often its parent system.
List of services
The CSIRT mission is carried out through the delivery of CSIRT services to its constituency. CSIRTs may offer several services, but there are cardinal ones that a CSIRT must offer to be considered a formal incident response team. At its most basic level, a CSIRT must be able to practise the following:
- Receive an incident report from a constituent. In order to receive an incident report from a CSIRT constituency, the constituency first needs to know the CSIRT exists. Constituents also need to understand what the CSIRT does and how its services are accessed, likewise every bit the service and quality levels it tin look. Thus, the CSIRT needs to have defined its mission and services, announced itself to its constituency and published guidance on how incident services are requested. This includes publishing an incident response policy, processes, procedures, forms and resources necessary to inform and enable constituencies to file incident reports.
- Analyze an incident report to validate and understand the incident. Once an incident report has been received, the CSIRT analyzes the report to validate that an incident or other type of activity that falls nether the CSIRT mission has indeed occurred. The CSIRT then determines if it understands the report and the incident well enough to create an initial response strategy that fulfills the goals of regaining control and minimizing damage. Part of being able to analyze an incident report and respond efficiently is having staff that tin can perform a variety of tasks. Members of the CSIRT should accept written plans, policies and procedures that document their specific roles and responsibilities.
- Provide incident response support. Depending on how the CSIRT is organized and the services offered, a CSIRT may provide incident response support via the following:
- on-site incident response services delivered directly to the constituent;
- incident response services delivered over email or the phone; or
- coordinated incident response services that combine and classify the efforts of multiple incident response teams across multiple constituents.
In some situations, an organization's CSIRT may only develop and oversee incident response strategies and services rather than implement them. For instance, other groups or departments, such as network engineers or system and data owners, may carry out the response strategy with the CSIRT managing the try.
CSIRT structures
How a CSIRT is structured depends on its parent organization'due south needs. For example, consider if 24/7 coverage is needed, the availability of trained employees, whether full- or office-time team members are required, and operating costs.
There are several mutual CSIRT structures, including the post-obit:
- Centralized CSIRT. In a centralized CSIRT, a single incident response team serves the entire organization, and all incident response resources are independent inside the dedicated unit of measurement. This model is well suited for pocket-size organizations or organizations with express geographic scope.
- Distributed CSIRT . In a distributed CSIRT, several independent incident response teams exist. The distribution of CSIRT resource may depend on wide geographic telescopic of the organization or the location of its major facilities. Other attributes that include whether a company is organized by a business unit of measurement structure or simply by the distribution of employees and information assets may likewise influence the CSIRT's distribution. Additionally, most distributed CSIRT models require a coordinating CSIRT.
- Coordinating CSIRT . This CSIRT manages other, oftentimes subordinate, CSIRTs. This CSIRT coordinates incident response activities, information menstruum and workflow among distributed teams. A analogous CSIRT may not provide any independent incident response services itself. Instead, information technology focuses on the efficient and constructive apply of resource in the distributed teams. For example, CERT/CC, the Software Technology Plant'due south (SEI) computer emergency response squad, is a coordinating CSIRT that orchestrates activities among national, governmental and regional CSIRTs.
- Hybrid CSIRT . A hybrid CSIRT combines attributes of centralized and distributed CSIRTs. The central CSIRT component is ofttimes total time, and the distributed component is equanimous of subject matter experts (SMEs) who may not be attached to incident response activities except as needed during security events. In this model, when the central CSIRT detects a potential consequence, it analyzes the incident and determines the response needs. Then, the appropriate distributed CSIRT experts tin can be called up to assist in these activities. Though a hybrid CSIRT relies on SMEs who are non full-time CSIRT members, it is definitively a formal incident response team. The hybrid CSIRT's distributed units of experts are designated every bit incident response professionals with defined roles and responsibilities and receive formal incident response training. They may also be required to obtain and maintain incident handler certifications.
- CSIRT/SOC hybrid . In this specialized hybrid model, the security operations centre (SOC) is responsible for receiving all alerts, alarms and reports indicating potential incidents. If the SOC requires assistance with boosted assay, the CSIRT is activated. In general, the SOC acts as a forepart finish for the CSIRT, performing incident detection, and then passes incidents to the CSIRT to handle.
- Outsourced CSIRT . An outsourced CSIRT tin be a helpful choice for companies that lack the resources or staff to build an in-house team. This CSIRT model involves staffing an internal CSIRT with contractors rather than employees or outsourcing CSIRT tasks and services that may exist just occasionally needed, such as digital forensics.
How to build a CSIRT
Developing an effective incident response strategy means an organization can detect and respond to a calculator or infosec incident in a style that limits damage and keeps recovery costs as low every bit possible.
When developing an incident response team, consider the following:
- Decide what types of technical backgrounds, roles and responsibilities are required.
- Assign a team leader to oversee CSIRT efforts, too as communicate incidents and progress to the executive leadership.
- Determine the proper CSIRT organizational model and the required functioning hours for the team.
- Create security plans, policies and procedures for a multifariousness of potential threats and incidents.
- Provide CSIRT members with routine cybersecurity didactics and awareness grooming.
- Carry systemwide gamble assessments.
- Identify critical incident response assets, including data, business organization processes, technology and people.
- Have a well-documented nugget direction plan.
- Implement a configuration managementprogram to ensure all software is patched and any updates are tested and applied in a timely style.
- Execute a defensive network architecture using routers, firewalls, intrusion detection and preventionsystems (IDSes/IPSes), network monitors and security operations.
CSIRT fellow member roles
An effectively functioning CSIRT requires an array of members with various skills and responsibilities. There is no 1-size-fits all approach, however. Organizations must staff and train employees to meet their specific security incident response needs.
Several factors affect the organization of CSIRT roles, including the system's risk profile and CSIRT construction. In general, CSIRT members include the following:
- CSIRT team lead. This executive role, typically occupied by the chief information security officeholder (CISO), communicates incidents with C-suite executives and coordinates the CSIRT upkeep.
- Incident manager. This function coordinates CSIRT meetings, ensures accountability from CSIRT members across the organization and determines whether incident findings should be escalated to executives.
- Supporting CSIRT staff. These technical roles, such as the security analyst, incident handler, shift lead or forensics investigator, are responsible for incident detection, response and reporting activities.
- Cross-functional CSIRT roles. To carry out its mission, a CSIRT often incorporates legal, human resource (Hr) and public relations (PR) professionals into the team. For instance, a member of the legal team advises on potential lawsuits from shareholders or employees, also as the incident disclosure process. An HR part in the CSIRT manages personnel problems and communicates incidents to employees. PR staff handle press releases; employee, partner, customer and stakeholder communications; and media inquiries regarding security incidents.
CSIRT members' skills and responsibilities
CSIRT staff play a critical role in upholding the CSIRT mission and service. An effective CSIRT requires staff members to maintain a diverse range of technical and nontechnical skills.
Technical skills
CSIRT staff need a baseline of technical skills and security knowledge to perform daily tasks. A general understanding of security principles, vulnerabilities, programming and network protocols found this baseline. In add-on, CSIRT staff should exist trained in the post-obit technical skills for incident handling:
- identifying intruder tactics and techniques;
- securing CSIRT communications through encryption;
- analyzing incidents to determine how to respond effectively; and
- maintaining incident records and reports.
Nontechnical skills
CSIRT work is service-based. Thus, all CSIRT staff must demonstrate diplomacy and communicate competency in interactions with constituents.
- Willingness to follow instructions. Staff should exist familiar with defined CSIRT procedures and policies and the importance of upholding them.
- Communication. Staff should demonstrate constructive written and interpersonal communication skills necessary to fulfill duties such equally documenting incident reports or presenting technical briefings.
- Collaboration. Due to the cooperative nature of the CSIRT construction, members must be committed team players to ensure collective morale, productivity and agility.
- Fourth dimension direction. Staff should understand how to utilise provided criteria to prioritize various CSIRT activities and determine when to ask for assist from direction.
- Analytical reasoning. CSIRT staff need to think out of the box to conceptualize assailant techniques and problem-solve in potentially volatile situations.
- Stress direction. The enervating nature of incident response and risk of security staff burnout warrant special attention to managing stress, equally well as piece of work-life balance.
- Continuous learning. Incident response is a constantly changing area of expertise. Thus, CSIRT members must be inquisitive people and embrace opportunities to further their skills through preparation, certification or mentorship.
CSIRT management
It is of import to have a dispersed and well-managed CSIRT. Most CSIRTs are structured to maintain 24/vii monitoring. This is done by dividing operating hours into three shifts, each with a designated shift lead. During their shifts, shift leads should communicate their work and findings with other shift leads. This data should then exist relayed to the CSIRT team pb or executive staff member to maintain transparency with the rest of the organization.
Larger companies should not merely separate employees by fourth dimension, but as well geographic location. Smaller companies may observe it more than toll-effective to outsource CSIRT processes for afterwards hours.
SOC vs. CSIRT vs. CERT
Organizations may employ one or more of the three main types of incident response teams: CSIRTs, SOCs and CERTs. Sometimes, these terms are used synonymously, though differences do exist, depending on the organisation's use of the term(south).
The about unique of the iii is the SOC. This defended facility monitors and defends technology and hardware and acts as a control-and-control center for an organization, region or state. It protects networks, servers, applications and endpoints. A SOC's responsibilities, however, extend beyond that of merely incident response.
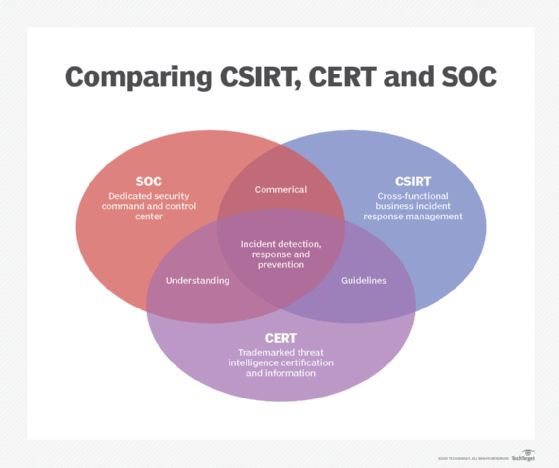
CSIRT, CERT and the less-often-used reckoner incident response squad (CIRT) are often used interchangeably. In general, CSIRTs, CERTs and CIRTs all handle incident response, though their specific tasks may vary by organization. The terminology used by an organization should be adequately defined, along with the goals, structure and use of resources necessary to properly respond to incidents.
It is important to annotation that CERT is a registered trademark of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU). Organizations may use the CERT mark after achieving authorization. However, some organizations -- probable unaware it is trademarked -- still use it to define their incident response teams.
This was concluding updated in March 2021
Continue Reading About computer security incident response team (CSIRT)
- To improve incident response adequacy, showtime with the right CSIRT
- NIST incident response program: 4 steps to improve incident handling
- Free cybersecurity incident response plan template
- How attackers counter incident response after a data breach
- Offset CSIRT services framework
Source: https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/Computer-Security-Incident-Response-Team-CSIRT
0 Response to "What Are the Components to Building an Effective Csirt Team?"
Post a Comment